New Imaging Better Identifies Sources of Chronic Pain
/By Pat Anson, PNN Editor
A new approach to diagnostic imaging that combines the use of positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could help identify the causes of chronic pain better than current methods, according to a new study at Stanford University School of Medicine.
PET scans that identify increased glucose metabolism in the body – known as 18F-FDG PET -- are currently used by oncologists to detect where tumors are located. Stanford researchers say the same approach could also be used to more precisely locate inflammation in injured nerves and muscles.
"In the past few decades, we have confirmed that anatomic-based imaging approaches, such as conventional MRI, are unhelpful in identifying chronic pain generators," said Sandip Biswal, MD, an associate professor of radiology at Stanford University School of Medicine.
"We know that 18F-FDG PET has the ability to accurately evaluate increased glucose metabolism that arises from to acute or chronic pain generators. As such, in our study we examined PET/MRI as a potential solution to determine the exact molecular underpinnings of one's pain."
In the study, 65 chronic pain patients underwent 18F-FDG PET and MRI scans from head to toe. The PET/MR images were then evaluated by two radiologists to determine if more glucose uptake occurred in painful areas or in other parts of the body. Increased glucose metabolism was detected in 58 of the 65 patients.
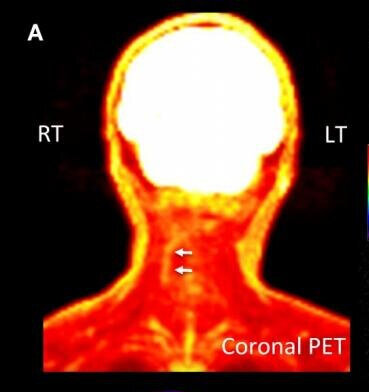
One such patient was an adult male who lived with decades of chronic pain in his neck as a result of an injury experienced at birth. PET/MR scans — such as the image on the right — identified muscles in his right neck near a spinal nerve where there was elevated glucose uptake.
This finding encouraged a surgeon to explore the area. The surgeon found a collection of small arteries wrapped around the nerve. When the arteries were ablated (removed) by the surgeon, it relieved pressure on the nerve and the patient reported tremendous relief.
Cipriano, et al., Stanford University
As a result of PET/MR imaging, 40 patients in the study had their pain management plans modified, including some who had procedures that their doctor had not anticipated, such as surgery to relieve foot pain and the placement of blood patches to treat cerebrospinal fluid leaks.
"The results of this study show that better outcomes are possible for those suffering from chronic pain," said Biswal. "This clinical molecular imaging approach is addressing a tremendous unmet clinical need, and I am hopeful that this work will lay the groundwork for the birth of a new subspecialty in nuclear medicine and radiology.”
Biswal recently presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. They’ve also been published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.