My Story: Make Your Doctors Accountable
/By Crystal Moody, Guest Columnist
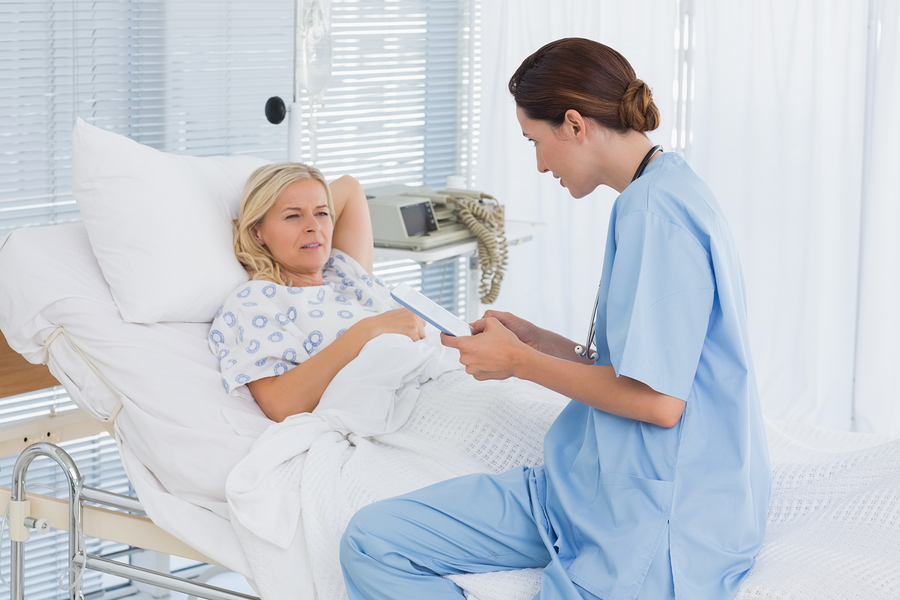
From a full-time medical education coordinator to full-time chronic pain patient, I am now trying to maneuver my way through the world from the other side of the operating table. And it is a completely different ballgame. Gaslighting, patient-blaming and condescension are daily players in this game.
I live with chronic back and neck problems, some caused by medical errors, and have undergone multiple spinal surgeries and procedures. I was legally labeled as “physically disabled” in 2018 by Social Security, but it took three years in California and I had to hire an attorney to make that happen. Every player in this game gets paid, except the patient.
It was the beginning of 2016 when I realized I was never going to be able to work in medicine in my former capacity again. However, even if my body was broken, my mind was not. I re-enrolled in college, wanting to keep my mind fresh in between surgeries.
In 2018, I completed my BA in Organizational Leadership at Azusa Pacific University (online and from bed). I then completed my Masters in Public Health from Los Angeles Pacific University in 2021. I am now pursuing a doctorate in Social Work.
I hope that my work and life experiences will allow me to help others, in the same ways that I have needed help. I want to help people with chronic, debilitating and life-threatening illnesses.
CRYSTAL MOODY
In the beginning of my illnesses, I did not understand why I could not just let things go. As time passed, I realized it was because I was witnessing doctors, specialists and clinicians who had no clue what they were doing. Even worse, I was beginning to realize that every doctor I consulted with seemed to count on the fact that I would not have any medical knowledge. They tried to placate or downplay my concerns, and send me on my way.
Initially, I thought it was because of my own ignorance as a patient. But in appointment after appointment, the truth became blatantly clear. If I had had no educational, personal, and/or professional experiences in medicine, they could have fooled me in every visit, every time.
My goal now is to train our doctors and specialists to be more patient, kind, empathic and ethical, by teaching patients how to be investigators of their own health information. Patients need to learn how to advocate for their own health during an era of “sloppy medicine.”
One such lesson is to teach patients where and how to hold their doctors and clinicians accountable. Never check hospital or medical practice reviews of your doctor. Those reviews are biased. As an ex-hospital employee, I can tell you who gets those reviews. Patients whose outcomes are successful and more likely to give positive reviews are noted by hospital employees. They send those patients the evaluation forms.
In the hospital where I worked, many evaluation forms were completed by other hospital employees. Some employees were even patients of the doctors they work with. How is that not a conflict of interest?
Always check for independent reviews through online sites such as HealthGrades. They are much better resources for patients with complex medical histories. You need to know who you are going to be working with, and it is immensely helpful to see other patients’ unbiased reviews of doctors. No one is a better professional in being and knowing you than YOU.
It should no longer be a one-way-street, with doctors doing all the talking during appointments. If patients know the right questions to ask, they will be better prepared to challenge the doctor for answers and direction. Patients deserve to get the most out of every visit. Additionally, I encourage you to observe if the doctor has a partner or assistant join them in your visits.
You should never go to an appointment alone, if you do not want to. If someone can’t physically be there, you can also make a FaceTime call to have a second set of “eyes and ears” at your appointments. The clinicians document your visits and sometimes bring reinforcements. You should, as well. Your input is valuable, and you should be documenting as much or more than your doctor.
The sad fact is that you are worth more to a doctor when you are sick than when you are well. They send you back and forth between their colleagues and specialists. It is time to cancel the hamster wheel of medicine and rebuild it through decency and transparency, with truly informed consent by both patients and doctors.
A poor doctor should not have the same status and pay as a good doctor, but they often are. What keeps a doctor honest if they earn the same despite their poor patient outcomes? Ultimately, for doctors to perform better, patients must be willing to hold them accountable when necessary.
Disabled patients should know there is no guilt or shame in disability, and that disability does not equal stupidity. There is opportunity for positivity in every negative situation.
Crystal Moody lives in California.
Do you have a “My Story” to share? Pain News Network invites other readers to share their experiences about living with pain and treating it.
Send your stories to editor@painnewsnetwork.org.