Fatal Overdoses Show First Decline in 5 Years
/By Pat Anson, PNN Editor
There’s good and bad news in the latest report on the overdose crisis in the United States.
Preliminary data released by the CDC show that there were an estimated 107,543 drug deaths in 2023, a 3.1% decline from 2022 and the first annual drop since 2018. The rate of confirmed overdoses fell even more -- by 5.1 percent – a number subject to change as lagging data and toxicology reports come in.
“We are encouraged to see the preliminary data that shows a decrease in the overdose death rate for the first time in five years, especially following the period of rapid double-digit increases from 2019-2021,” said White House Drug Control Policy director Dr. Rahul Gupta, in a statement.
That’s the good news.
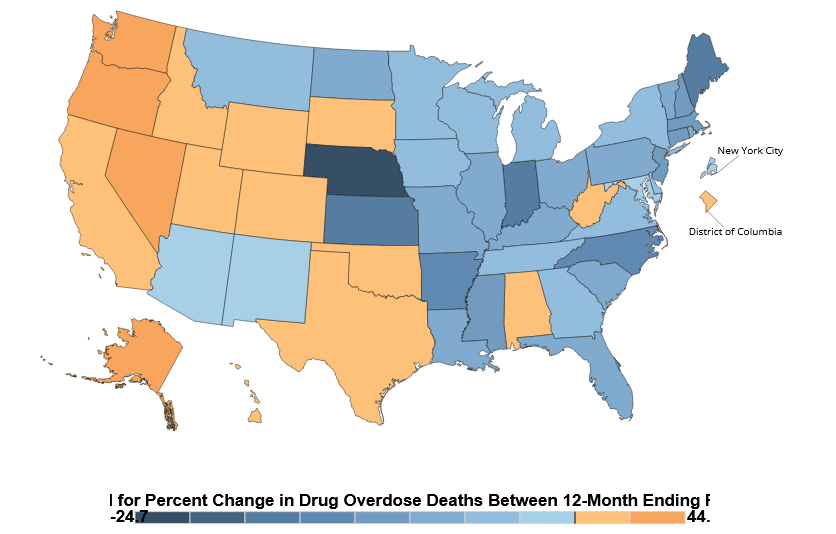
The bad news is that drug deaths kept rising in several western states, with Alaska (+44%), Nevada (+29%), Oregon (+30%) and Washington (+28%) showing substantial increases.
In contrast, overdoses declined in the East and Midwest, with significant decreases in Nebraska (-25%), Indiana (-18%), Kansas (-16%) and Maine (-16%).
The report did not offer any explanation for the wide variation between states and regions.
Percent Change in Drug Overdose Deaths 2022-2023
SOURCE: nchs
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) said over 74,000 deaths last year involved fentanyl – most of it illicit – and more than 36,000 deaths were attributed to methamphetamine.
Most overdose deaths involve multiple drugs, according to the NCHS, so “a single death might be included in more than one category” and be counted multiple times.
Although the numbers remain somewhat unreliable, this report and others suggest that fentanyl and other illicit drugs play a far greater role in the nation’s drug crisis than prescription opioids.
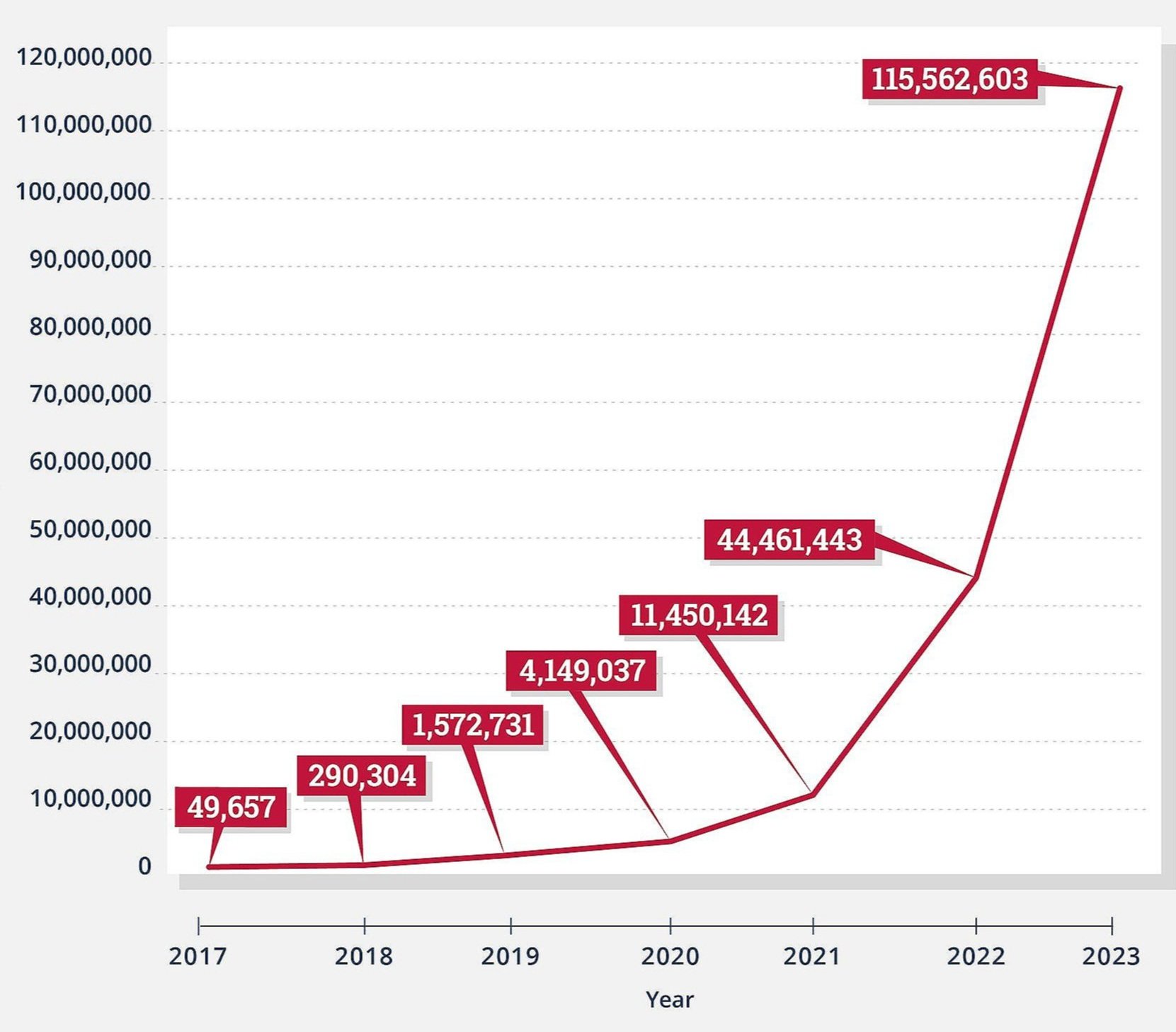
A study published this week in the International Journal of Drug Policy reported that law enforcement seized a record 115 million counterfeit pills containing fentanyl last year. That compares to only 4 million prescription opioid pills that were reported lost or stolen by the DEA in 2023.
Fake Pills Containing Fentanyl Seized by Law Enforcement
International Journal of Drug Policy
“Availability of illicit fentanyl is continuing to skyrocket in the U.S., and the influx of fentanyl-containing pills is particularly alarming,” wrote lead author Joseph Palamar, PhD, an Associate Professor in the Department of Population Health at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
“Both the number and size of drug seizures containing fentanyl have increased in the US between 2017 and 2023, with the majority of seizures –– particularly in pill form –– occurring in the West.”
Prescription opioids are mentioned only a handful of times in the DEA’s recent National Drug Threat Assessment, mainly within the context of their theft and diversion falling to the lowest levels in 12 years. That report also warns that counterfeit pills are increasingly being found with xylazine, a potent animal tranquilizer, and nitazenes, a synthetic opioid that is 40 times stronger than fentanyl