How the Curves in Your Spine Cause Back Pain
/By Dan Baumgard
Over 60% of us will suffer from lower back pain at some point in our lives. Without question, it’s the leading cause of disability across the globe.
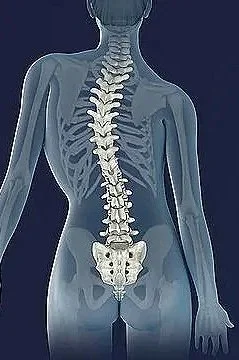
Your spine is comprised of 33 bones known as vertebrae, which are stacked one on top of the other. The resulting column is divided into five segments: cervical (in the neck), thoracic (at the same level as the chest), lumbar (at the level of the abdomen) and sacral (connecting with the pelvis). The fifth, the coccyx, is located at the very bottom of the spine (the tailbone) – and is very painful when injured.
The vertebrae are connected by multiple joints, including discs which allow the spine to move in multiple directions. Though we might think the spine should appear straight, it naturally curves forward and backwards so it can perform all of its important functions.
But many conditions can cause the spine to curve more than it should. This can not only lead to pain, but potentially a whole host of other health troubles too.
Dowager’s Hump
The spine also supports the weight of the body, protects the spinal cord and helps the body to bend, flex and twist. The thoracic region attaches to the ribs and naturally curves backwards – this curve is known as the thoracic kyphosis.
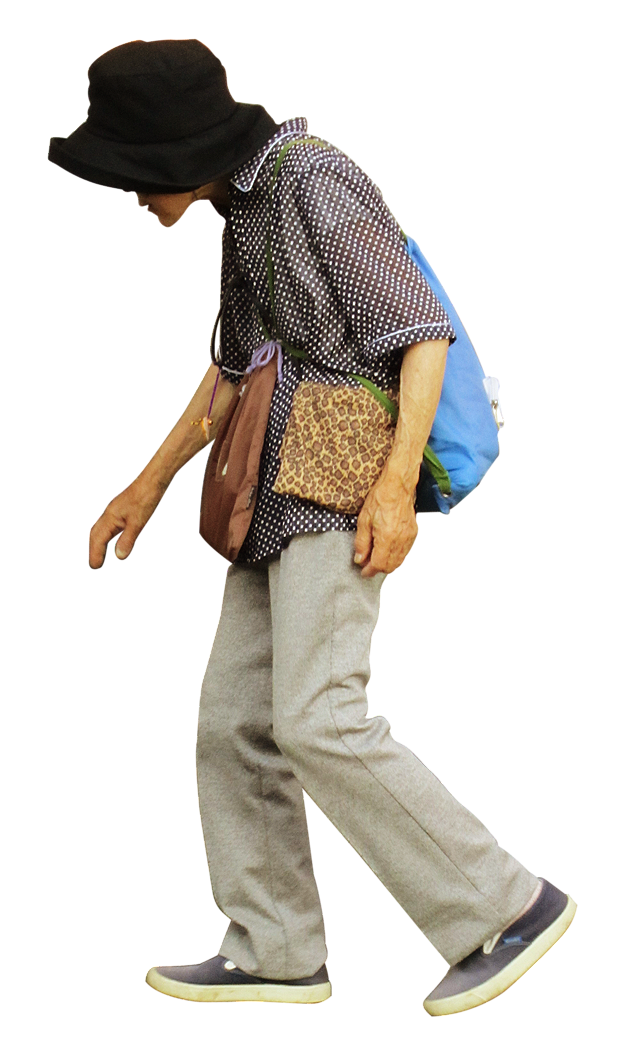
But sometimes, the curve of the thoracic kyphosis becomes more accentuated and visible – often as a result of osteoporosis (where bones become weaker), age-related changes to the back muscles and vertebrae, or long-term poor posture.
The medical name for this condition is hyperkyphosis, though it’s sometimes referred to as “dowagers hump” as it’s around two to four times more common in women.
A stooped posture with rounded shoulders (or “hunchback” appearance) is typically a sign of hyperkyphosis.
In some cases, it may become so extreme as to impact breathing since the chest can’t inflate properly. It can also affect swallowing since the neck becomes more horizontal and the gullet potentially narrowed.
Dowager’s hump
And of course pain and stiffness typically arise. This is a common theme for most patients with abnormal curvature of the spine, as the vertebrae lose their ability to move, and nerves arising from the spinal cord can become compressed.
Scoliosis
Another type of deformity that can occur in the spinal column affects not only how it bends forward and backwards, but also side-to-side.
Scoliosis occurs when the vertebrae either curve sideways, rotate in relation to each other, or collapse. This produces a variety of different deformities, ranging in size and severity.
The underlying causes of scoliosis are widespread. Sometimes bones can become deformed as a result of trauma, cancer or an infection (such as tuberculosis).
Scoliosis can also be present from birth, or arise from neurological disorders in early years – such as cerebral palsy.
As well as back pain, patients may also notice postural signs as scoliosis evolves. Their shoulder blades or ribcage can stick out more, and clothes may fit differently on their body.
SCOLIOSOS
Slipped and Fused Spines
Individual vertebrae in any part of the spine can sometimes also become displaced as a result of trauma, wear and tear, or certain health conditions (such as osteoporosis).
This means that instead of standing in a regular stack, a vertebra slips forward, and out of line. This condition is given the long and practically unpronounceable name, spondylolisthesis.
In doing so, this displacement can trigger nerve compression. If the sciatic nerve – the largest in the human body – gets compressed, it can lead to symptoms of sciatica. These are namely pain, pins and needles, or numbness in the back of the leg or buttock.
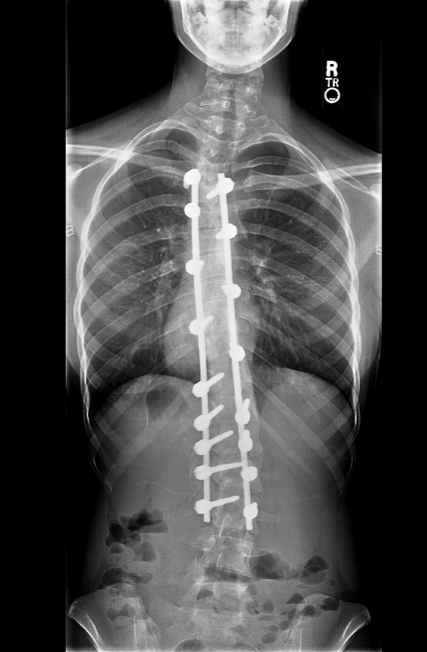
The vertebrae in the lower back can sometimes also fuse abnormally together. A condition called ankylosing spondylitis can trigger inflammation in the spinal joints and discs, which then harden over time. Another name for the condition is bamboo spine, since the now rigid and inflexible column resembles a tough stalk of bamboo.
FUSED SPINE
Managing Back Pain
Managing these conditions – and the pain they cause – will depend largely on the size of the deformity and what has caused it in the first place. Even a small spinal deformity can be significant.
For scoliosis for instance, braces to correct the spine as it grows may work to manage small defects in younger patients. But corrective surgery is often required to fix larger deformities and those which don’t respond to bracing.
Taking account of posture and bone health can also help prevent developing a spinal problem later in life. Using exercise to build a strong back and shoulders and avoiding slouching are solid measures, too. Managing associated conditions such osteoporosis with diet, medication and resistance training can also help.
Surgical intervention may be required in other situations – for instance, to decompress nerves that have become trapped or squashed.
Your spine is truly an architectural wonder. It’s far from a straight and rigid column – and capable of more than you’d ever expect. But this unique structure can lend itself to problems, especially when natural curves become deformities. The age-old adage “strengthen your back, strengthen your life” is a motto we should all be regularly reminded of, and to seek medical advice accordingly should back pain arise.
Dan Baumgardt is a medically-qualified clinical neuroscientist and anatomist. He is Senior Lecturer in the School of Psychology and Neuroscience at the University of Bristol
This article originally appeared in The Conversation and is republished with permission.