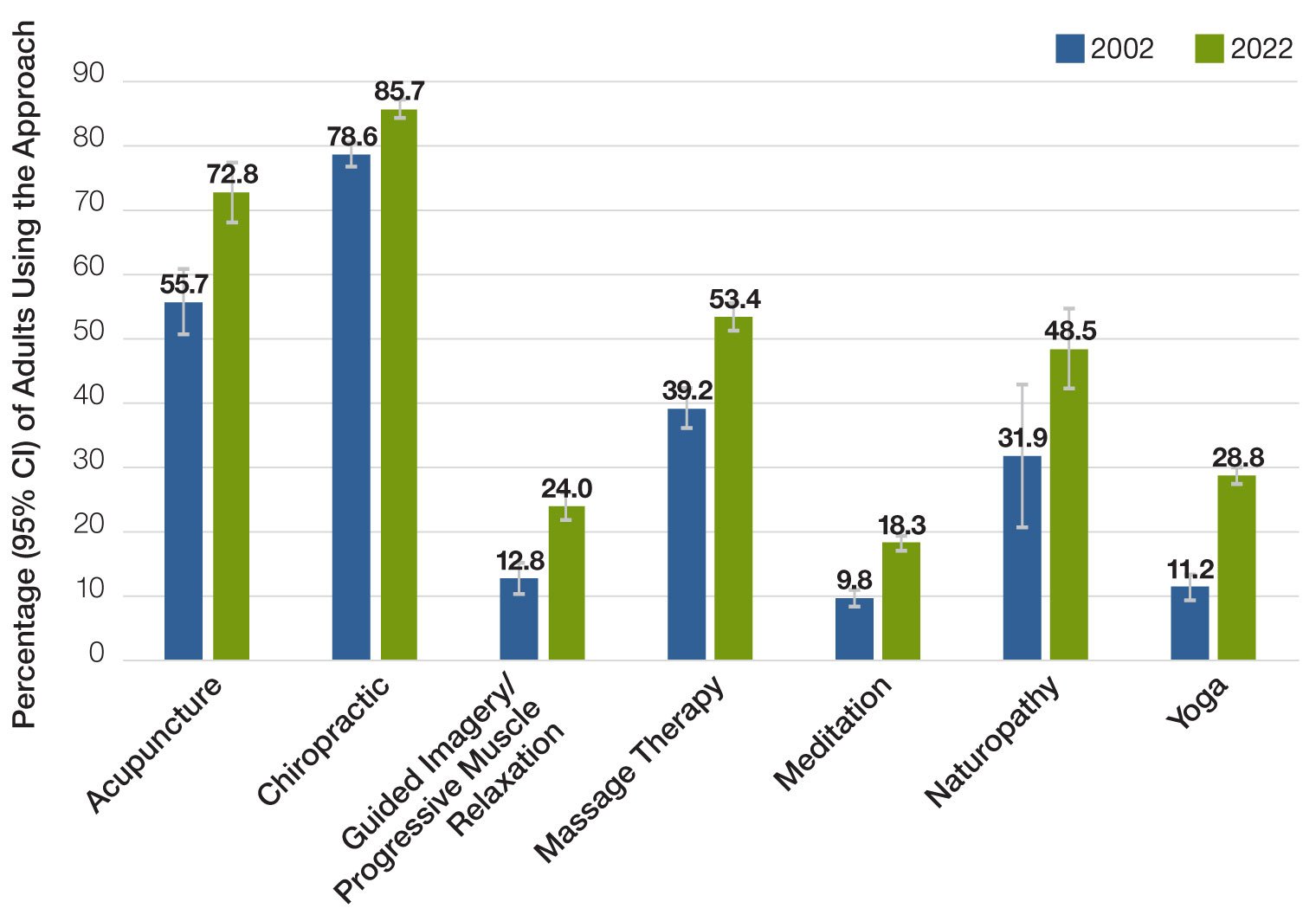
Does Mindfulness Really Help with Chronic Pain?
/By Neen Monty
“Mindfulness” is one of those words that’s been stretched so far it’s almost lost its meaning. We’re told it will calm our nerves, ease our pain, and maybe even transform our lives.
But what is mindfulness, really? And what can it actually do for people living with chronic pain?
The popular definition goes something like this: Mindfulness is the practice of focusing your awareness on the present moment, without judgment.
Does that make sense to you? It didn’t make sense to me the first time I heard it. It sounds so simple… but it’s not so simple to do.
Most people think mindfulness is meditation. It’s not. Mindfulness is a state of awareness, a way of relating to your thoughts and sensations, while meditation is a tool that helps you develop that state. Meditation is how we practice mindfulness, the training ground for the skill of self-awareness.
Clear? As mud…
Okay, let me try again. At its core, mindfulness rests on two ideas:
Paying attention to the present moment.
Doing so without judgment.
That second part is the hardest. It can take a lot of practice. But in practical terms, living mindfully is living in the present moment. It’s not wasting time worrying about a future that may never happen, or dwelling on a past that can’t be changed.
The Difference Between Pain and Suffering
Let’s use pain as an example. Being mindful doesn’t mean ignoring pain or pretending it’s not there. It means noticing it: “I feel pain right now” and stopping there.
What we usually do next is the problem: “Oh no, it’s back. The pain is so bad! It’s going to get worse. I can’t take this anymore.”
Those thoughts are the suffering part. They layer emotion, fear, and meaning on top of the physical sensation of pain.
Mindfulness helps peel that layer away. Pain still hurts, but without the extra story, the extra worry, the panic, the hopelessness and the emotional response. It’s just pain.
Pain then becomes something we can observe, without emotion, rather than something that swallows us whole. This distinction isn’t just philosophical. Brain imaging studies show that mindfulness changes the way we process both thoughts and sensations.
Meditation strengthens brain regions that regulate attention and emotion, such as the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex, while reducing reactivity in the amygdala, the brain’s alarm system. Other reviews confirm that meditation produces measurable neurobiological changes that are associated with greater emotional stability and self-regulation.
Over time, meditation helps the mind become less reactive. We learn to notice sensations, thoughts, and emotions without immediately trying to fight or fix them.
Instead of launching into fight or flight, we remain calm and in control. Meditation, in that sense, is kind of the laboratory in which mindfulness is trained.
The Limits of Mindfulness
Does mindfulness cure pain? No. It does not.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses find that mindfulness training has only small effects on pain intensity. What it does reduce is distress — the anxiety, fear, and emotional turmoil that often surrounds chronic pain.
That distinction matters. Mindfulness was originally designed as a treatment for stress and anxiety. And therefore, its benefits for pain are more indirect. It helps people who are fearful of pain or overwhelmed by it, to regulate their emotions and cope better.
But, if you’re already calm and accepted your pain without fear, mindfulness won’t make the pain go away. It won’t have much effect at all on your pain.
Most importantly, mindfulness is not a treatment for severe pain. You cannot be mindful and you cannot meditate, when you’re in severe pain. Mindfulness is not an intervention for 8 or 9/10 pain. That’s pure cruelty. I would even call that medical negligence.
Mindfulness is a treatment for fear and anxiety in the setting of chronic pain. In that sense, mindfulness may be helpful for someone in mild to moderate pain, where there is a lot of negative emotion surrounding that pain – such as fear, anxiety and catastrophising.
Mindfulness is a psychological tool, a treatment for fear and anxiety that’s been repurposed for pain.
And often oversold as something it’s not.
Why Mindfulness Is Still Worth Trying
Even within those limits, I still believe mindful living is the best way for me to live. It doesn’t make my pain stop. My pain is caused by disease, pathology and biology, not by anxiety or fear.
Mindfulness does make my days quieter. It keeps me from being dragged into fear or frustration. I don’t worry about the future and don’t dwell on the past. Mindful living keeps me grounded. In the present moment. Because that’s where life is happening – the here and now.
That’s what mindfulness is, living in the present moment.
Mindfulness won’t fix what’s broken in the body. Mindfulness cannot fix pathology. But it can help restore what pain often breaks in the mind: calmness, control, and your sense of peace in the middle of chaos.
And sometimes, that’s enough.
Neen Monty is a patient advocate in Australia who lives with rheumatoid arthritis and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP), a progressive neurological disease that attacks the nerves.
Neen is dedicated to challenging misinformation and promoting access to safe, effective pain relief. She has created a website for Pain Patient Advocacy Australia to show that prescription opioids can be safe and effective, even when taken long term. You can subscribe to Neen’s free newsletter on Substack, “Arthritic Chick on Chronic Pain.”