Women More Likely to Get Addicted to Pain Meds
/Pat Anson, Editor
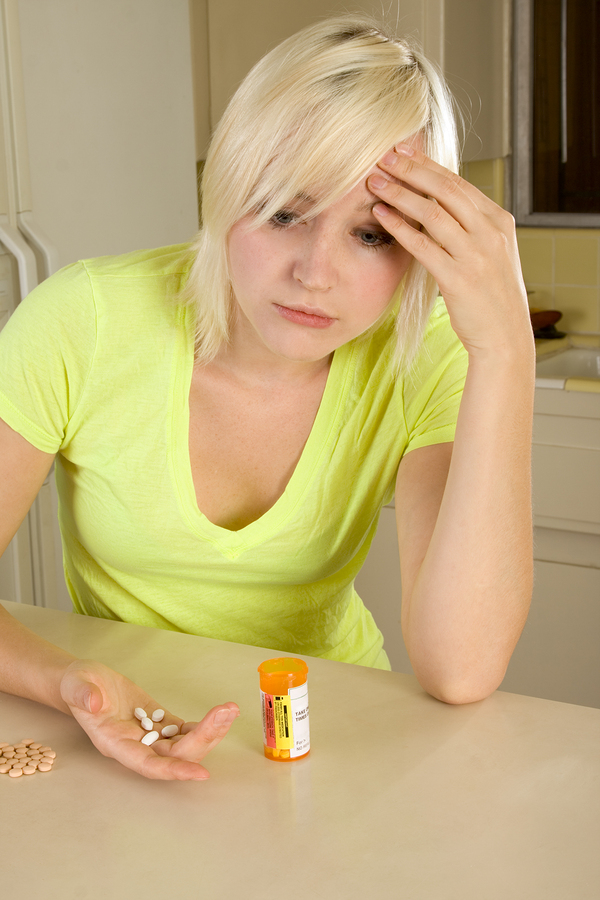
Over half the women being treated for addiction at methadone clinics in Canada say their first experience with opioids was a pain medication prescribed by a doctor, according to a new study.
Researchers at McMaster University in Hamilton recruited over 500 men and women being treated for opioid dependence at 13 clinics in Ontario. The aim of the study, which is published online in the journal Biology of Sex Differences, was to identify any significant gender differences between men and women attending the clinics. Participants provided researchers with detailed information about their health and lifestyle, as well as urine tests to measure their use of illicit and legal drugs.
Compared to men, women were found to have more physical and psychological health problems, more childcare responsibilities, and were more likely to have a family history of psychiatric illness.
While over half the women (52%) and about a third (38%) of the men reported doctor-prescribed painkillers as their first contact with opioids, only 35% of participants said they suffered from chronic pain during the study period.
"It's not clear why women are disproportionately affected by opioid dependence originating from prescription painkillers - it could be because they're prescribed painkillers more often due to a lower pain threshold, or it might simply be because they're more likely than men to seek medical care,” said lead author Monica Bawor of McMaster University.
“Whatever the reasons, it's clear that this is a growing problem in Canada and in other countries, such as the U.S., and addiction treatment programmes need to adapt to the changing profile of opioid addiction."
Only about a third (36%) of the study participants were employed or had completed a high school education (28%).
Men were more likely than women to be employed, and were more likely to smoke cigarettes. Men were also more likely to report having smoked marijuana, although rates of marijuana use were relatively high among both men and women, Nearly half (47%) said they had used marijuana in the month prior to the study.
"Most of what we currently know about methadone treatment is based on studies that included few or no women at all. Our results show that men and women who are addicted to opioids have very different demographics and health needs, and we need to better reflect this in the treatment options that are available,” Bawor said.
"A rising number of women are seeking treatment for opioid addiction in Canada and other countries yet, in many cases, treatment is still geared towards a patient profile that is decades out of date - predominantly young, male injecting heroin, and with few family or employment responsibilities."
Compared to studies from the 1990s, the average age of patients being treated for opioid addiction is older (38 vs. 25 years of age), and patients also started using opioids at a later age (25 vs. 21 years). There was a 30% increase in the number of patients becoming addicted to opioids through doctor-prescribed painkillers.
The number of opioid painkiller prescriptions has doubled in Canada over the last two decades. According to the World Health Organization, Canada consumes more opioid painkillers per capita than any other country.