New Test Identifies Poor Drug Metabolizers
/By Pat Anson, Editor
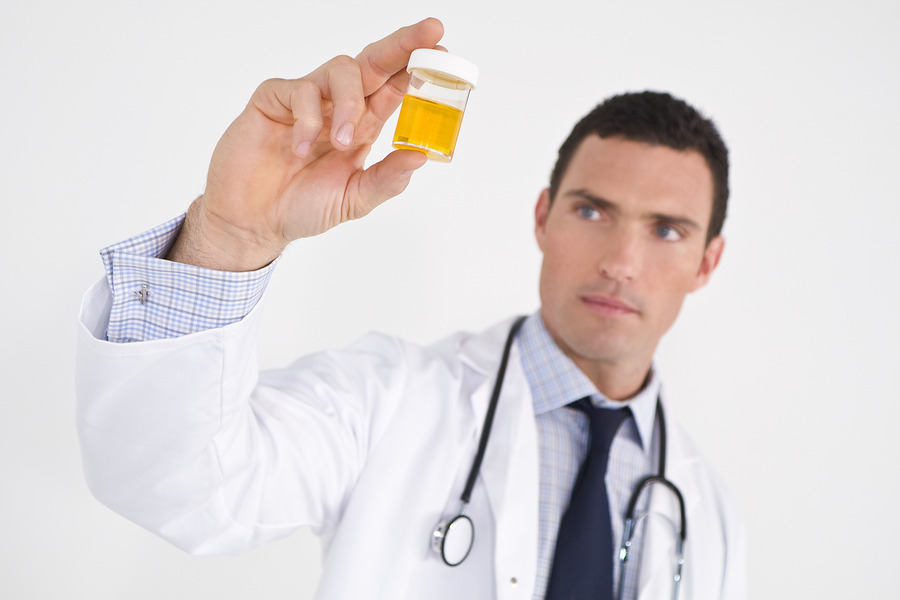
We hear regularly from readers who say they were discharged by their doctor after failing a urine drug test. Often it’s a case of an opioid painkiller not being found, which leads the doctor to believe a patient is selling or diverting their medication.
“The doctor said after 12 years of never having a bad urinalysis or anything ever happening, such as lost medication, asking to receive more or an early prescription, they said no medication was in my system. No one would retest and I was cut off cold turkey!” a pain patient recently told us.
“I went through hell trying to clear my name, horrible withdrawal with no doctor supervision or help, was labeled and thought I would die. This is a terrible way to treat anyone, especially someone with an untreatable life-long pain condition.”
Why are patients being falsely accused? In many cases, it’s because they have genetic differences that make them a low or high metabolizer of certain opioids. A painkiller like hydrocodone, for example, can quickly be utilized or pass through their system -- with little or no trace of the drug left behind.
Urine drug tests that are typically done in a doctor’s office -- known as point-of-care (POC) tests – do not identify these poor drug metabolizers. And studies show that about 30 percent of POC tests have “false negative” findings about opioid medication.
“Just because it may not show up in their system may not mean that they’re not taking it. There are two rational justifications for that. One is a bad drug test and the other is a patient may be a poor or ultra-rapid metabolizer of the medication that is being prescribed to them,” said David McCrea, CEO of Insight Diagnostics.
“I think most (doctors) understand how faulty the point of care tests can be, especially pain physicians. But I’m not sure the average physician understands how much a person’s individual metabolism can affect their drug test.”
Insight Diagnostics recently began offering a new testing service – called Genetically Enhanced Medication Monitoring (GEMM) – that combines a saliva-based genetic test with a laboratory test that more precisely identifies drug molecules in a patient’s urine. When used together, the two tests can reassure a doctor that a patient is telling the truth about their drug use.
“This is a game changing test that will allow physicians to uncover why some patients say, ‘I am taking my medication, I am taking it as prescribed and it’s just not showing up.’ This is scientific information that can validate a patient’s assertion,” McCrea told PNN.
“Certainly there are going patients that are going to try and game the system. But for those patients that are in chronic pain and are doing what they signed their pain contracts to do, this allows for a deeper dive for the physician to determine whether the patient is actually taking their medication, or they can’t metabolize it or they over-metabolize it.”
McRae says GEMM costs "a couple hundred dollars at the most” and is covered by Medicare and most private insurers. It doesn’t offer immediate results, as POC tests do, but the findings are far more accurate. They can also help physicians identify medications that will be metabolized normally by a patient and will be more effective.
Genetic tests cannot be used to explain “false positive” findings from a POC test – the detection of a drug that isn’t actually there. But laboratory testing can. Retesting a urine sample is more expensive, but it can help prevent patients from being falsely accused – something that happens far too often.
A recent survey of doctors and health care providers by PNN and the International Pain Foundation found that 20 percent had discharged a patient for failing a drug test in the past year. About four percent of patients said they had been "fired" by a doctor over a failed test.
“I failed a drug test which said I was positive for 4 drugs I have never taken in my life and was negative for opiates when I was taking Norco. My doctor abruptly stopped treating me even after I demanded my sample be retested,” a patient told us. “These drug tests are not reliable and should not be used and pain contracts should be illegal since they are forced on the patient.”
Click here to see a short promotional video about GEMM.