Bill Expands Pain Care Options and Lowers Cost for Medicare Patients
/By Dr. Lynn Webster
Everyone who reads this publication understands chronic pain is often treated as a symptom. However, for tens of millions of Americans, it is a disease state. It reshapes the nervous system, erodes function, and can narrow life experiences to what hurts least.
It’s also becoming more common. Federal survey data show that roughly a quarter of U.S. adults report chronic pain, and a substantial subset report “high-impact” chronic pain severe enough to limit work or daily activities.
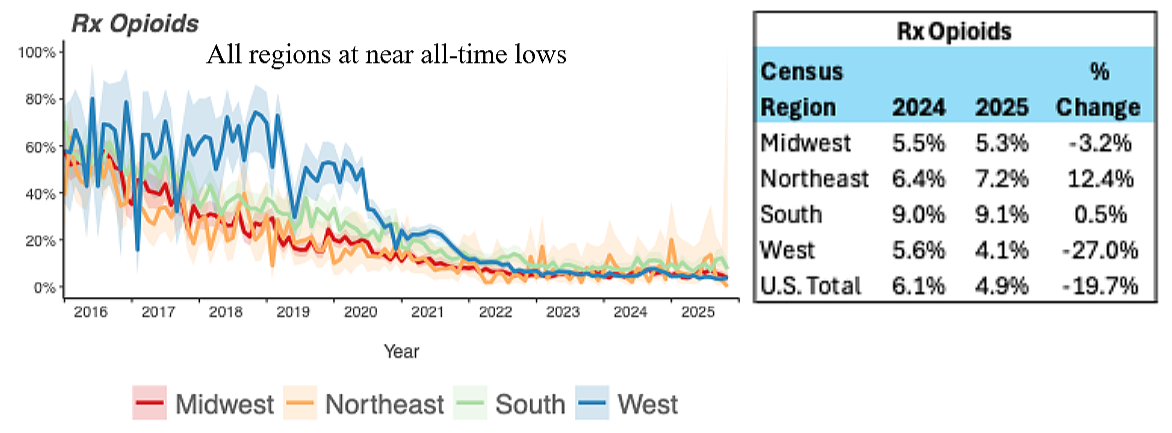
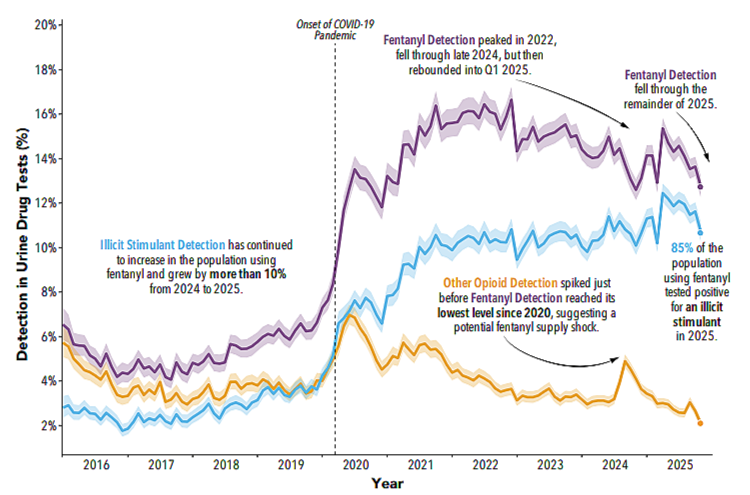
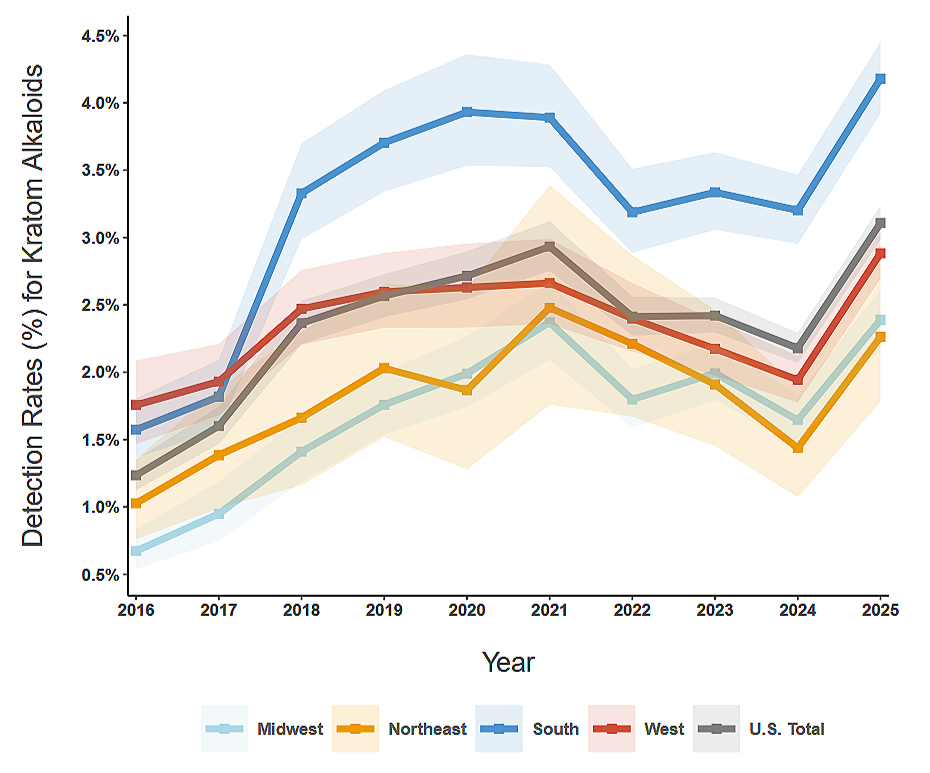
The public conversation about pain has been dominated for a decade by opioids, and for good reason. Opioids carry real risks, especially with long-term use, and the nation has paid dearly for indiscriminate prescribing and poor safeguards. But focusing only on opioids can obscure a quieter policy failure. Many patients who are trying to avoid opioids can’t reliably access effective non-opioid options, particularly in Medicare Part D.
That gap is structural, as well as clinical. Medicare Part D plans commonly use utilization management tools, prior authorization and step therapy among them, that can delay or block access to certain medications. For older adults living with neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, or other chronic pain conditions, delays can mean months of impaired function while paperwork circulates, appeals are filed, and “fail-first” sequences play out.
In practice, these barriers can shape prescribing in ways that have little to do with what a clinician believes is best. When a newer non-opioid medication is placed on a high cost-sharing tier, requiring multiple authorizations, or is only covered after a patient “fails” other therapies, the path of least resistance too often becomes the therapy that is easiest to access — not necessarily the therapy that best matches the patient’s needs.
A bipartisan bill now before Congress is designed to address a narrow but consequential piece of that problem for Medicare beneficiaries: the Relief of Chronic Pain Act of 2025 (S. 3064). Its basic logic is simple: If policymakers want less reliance on opioids, coverage rules should not systematically disadvantage non-opioid alternatives.
The bill would do three things for qualifying non-opioid chronic pain management drugs in Part D plans, beginning in 2026. It would waive the deductible, require plans to place the drug on the lowest cost-sharing tier, and prohibit prior authorization and step therapy, which forces patients to try an opioid first.
Importantly, S. 3064 is not written as an open-ended mandate for all pain treatments. It defines qualifying drugs as FDA-approved non-opioid products for chronic pain conditions that do not act on opioid receptors and, in general, are not simply interchangeable with an existing therapeutically equivalent product.
It also defines “chronic pain condition” with specific examples, including diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, endometriosis, fibromyalgia, musculoskeletal pain, neuropathic pain, post-herpetic neuralgia, and trigeminal neuralgia.
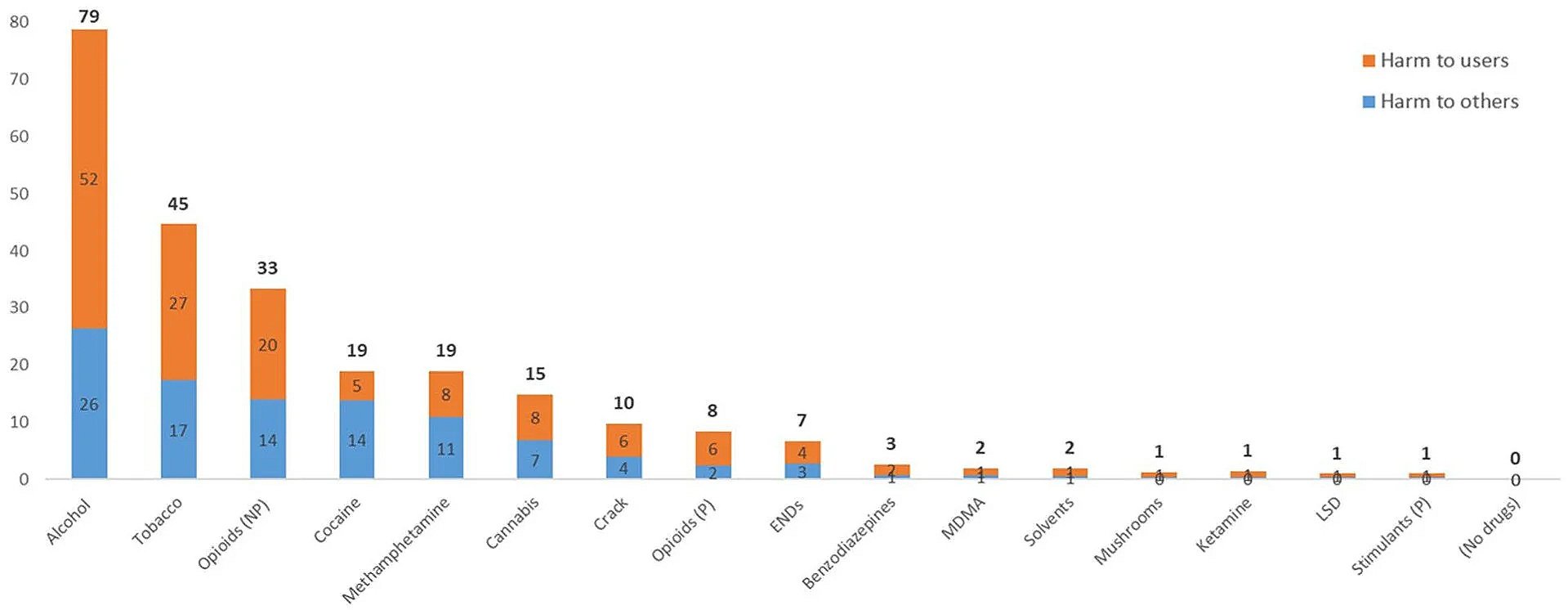
Why does a target change like this matter? Because pain is not just discomfort; it is an economic and social force. Chronic pain drives health care use, disability claims, and lost productivity on a massive scale, with major national cost estimates in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually.
When coverage delays effective treatment, the downstream costs do not disappear. They shift to more Medicare patients falling, more deconditioning, more depression and isolation, more emergency visits, and -- in some cases -- greater exposure to higher-risk medications.
Coverage policy won’t solve chronic pain by itself. The best care is multimodal: movement, behavioral strategies, physical and occupational therapy, interventional options when appropriate, and medications when they add meaningful benefit. Opioids will remain appropriate for a subset of people with chronic pain. But insurance design can either support alternative therapies or quietly undermine them.
S. 3064 asks Congress to make one pragmatic adjustment: Stop treating certain non-opioid options as luxuries for Medicare beneficiaries and start treating timely access as a basic component of safer pain care.
Unfortunately, since its introduction in Congress last October by Sen. Steve Daines (R-MT) and Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA), the bill has languished in the Senate Finance Committee. No hearings on S. 3064 are currently scheduled.
Readers who want to follow the proposal can review the bill text and legislative updates here. A public petition supporting the measure is also circulating for those who wish to add their names. If you want more options that are accessible and affordable, you should consider signing the petition and spreading the word.
Lynn R. Webster, MD, is a pain and addiction medicine specialist. He writes and lectures on pain policy, patient safety and evidence-based treatment. Webster is currently a Senior Fellow for The Center for U.S. Policy. He is the author of the forthcoming book, “Deconstructing Toxic Narratives: Data, Disparities, and a New Path Forward in the Opioid Crisis.”